Systemic Mastocytosis: A Rare Disease with Many Faces
Systemic Mastocytosis (SM) is a rare blood disorder, classified as a myeloproliferative neoplasm. It occurs when mast cells—a type of white blood cell involved in allergic reactions and immune defense—accumulate abnormally in one or more organs. These organs may include the skin, bone marrow, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, or intestines.
SM can range from mild, asymptomatic forms to aggressive disease that significantly impacts organ function and survival.
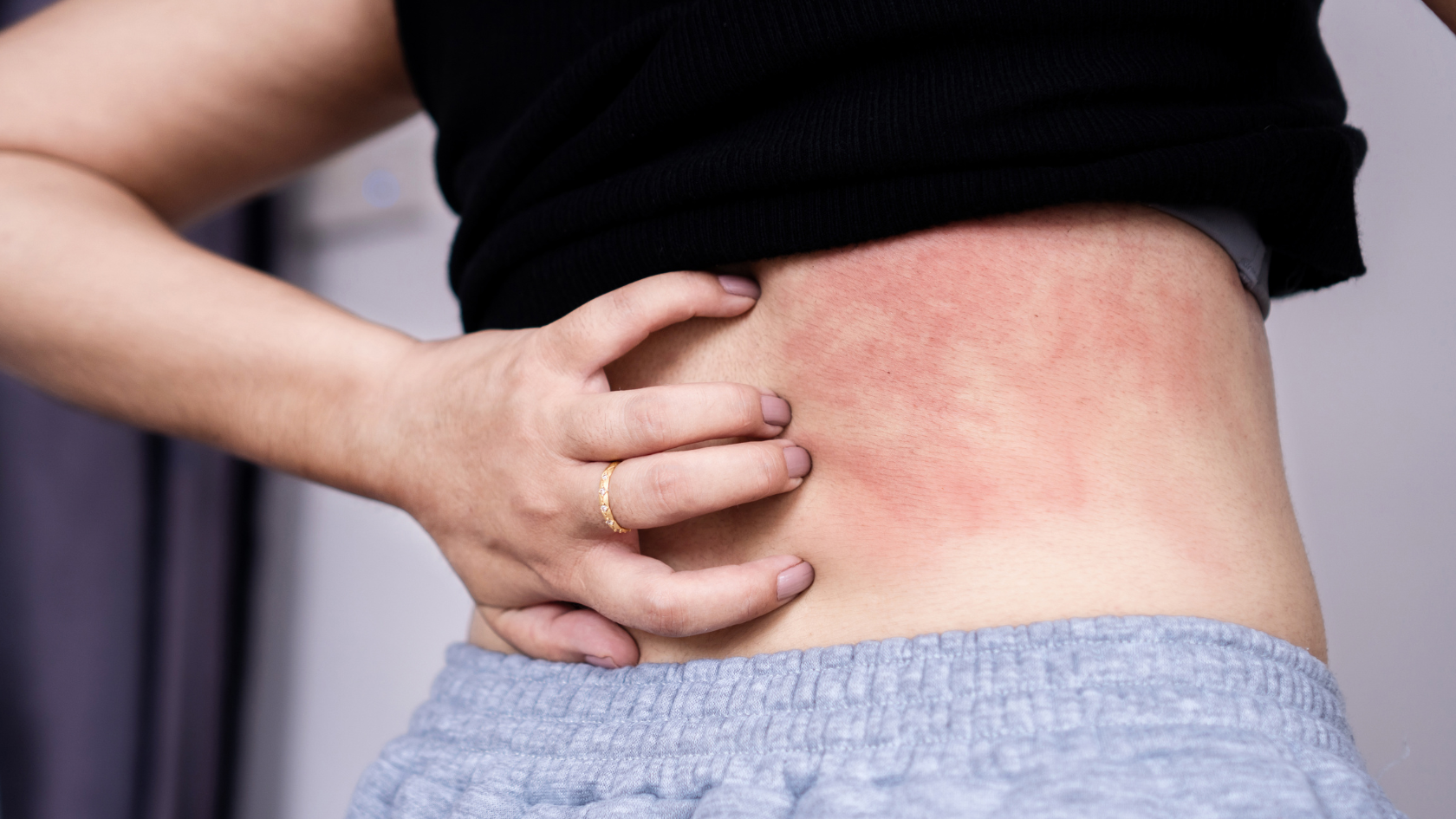
Itching and redness are some of the early signs of Systemic Mastocytosis
Types of Systemic Mastocytosis
The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies several SM subtypes:
- Cutaneous mastocytosis (CM): Mostly affects the skin, common in children.
- Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis (ISM): Slow-progressing, often mild symptoms.
- Systemic Mastocytosis with an associated hematologic neoplasm (SM-AHN): SM combined with another blood cancer.
- Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis (ASM): Rare, fast-progressing, with organ damage.
- Mast cell leukemia (MCL): Extremely rare, very aggressive.
- Mast cell sarcoma: Malignant tumor of mast cells.
- Mastocytoma: Localized mast cell tumor, usually on the skin.
The clinical course and prognosis vary widely depending on the subtype.
Symptoms
Symptoms can involve multiple systems due to mast cell accumulation and release of inflammatory substances (mediators):
- Skin: Itching, redness, flushing, maculopapular lesions
- Gastrointestinal: Heartburn, sharp abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Cardiovascular: Low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, arrhythmias, fainting, headaches
- Respiratory: Shortness of breath
- Musculoskeletal: Bone pain, osteoporosis, pathological fractures
- Other: Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly), fluid buildup (ascites), enlarged spleen, malabsorption, weight loss – more common in ASM.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing this rare disease is complex and usually requires a combination of clinical, laboratory, and biopsy tests.
Key diagnostic steps include:
- Cutaneous assessment: Look for maculopapular skin lesions.
- Bone marrow or organ biopsy: Detects multifocal clusters of mast cells.
- Laboratory tests:
- Serum tryptase >20 ng/mL indicates increased mast cell activity.
- Detection of c-kit mutation in mast cells.
- Immunohistochemistry: CD117(+), CD2(+) and/or CD25(+) markers on mast cells.
Diagnostic criteria
At least one major and one minor criterion or three minor criteria are required for a diagnosis of SM.
Treatment
Management depends on disease subtype, patient age, and overall health:
- General measures for all SM patients:
- Patient education
- Avoiding mast cell triggers (e.g., certain foods, medications, insect stings)
- Symptomatic treatment for mediator-related effects (e.g., antihistamines)
- For ASM with organ damage:
- Midostaurin (first-line therapy; effective in ~60% of patients)
- Other options: Interferon-α, cladribine, glucocorticosteroids
- Experimental therapies: Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., gemtuzumab)
- Rarely: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
What to do in case of a suspect?
Besides contacting your doctor, you can also report your symptoms and ask for a free risk of rare diseases assessment.
Click on “report a case” at the top right to start.
References